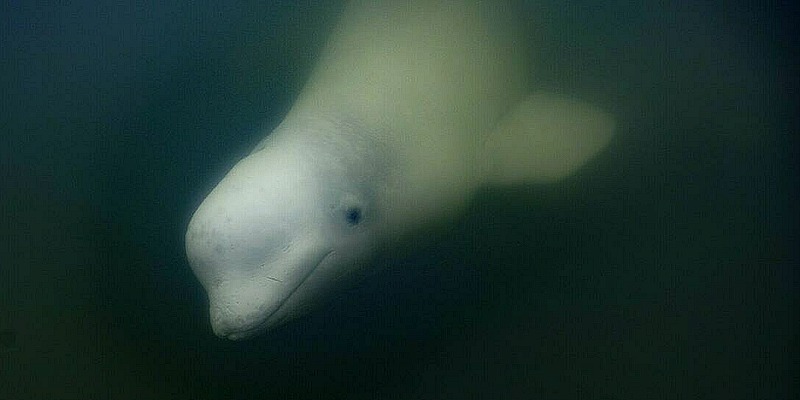
CHURCHILL, Canada: Half a dozen beluga whales dive and reemerge around tourist paddle boards in Canada’s Hudson Bay, a handful of about 55,000 of the creatures that migrate from the Arctic to the bay’s more temperate waters each summer.
Far from the Seine river where a beluga strayed in early August north of Paris, the estuaries that flow into the bay in northern Canada offer a sanctuary for the small white whales to give birth in relative warm and shelter.
In the murky bay, the belugas, with small dark eyes and what look like wide smiles, seem to enjoy the presence of a cluster of tourists who traveled to the remote town of Churchill — home to some 800 people and only accessible by train or plane — to observe the cetaceans.
For more than seven months of the year, between November and June, the bay is frozen.
The thaw marks the return of the belugas to the haven, where they are protected from orcas and feed on the rich food found in the estuaries.
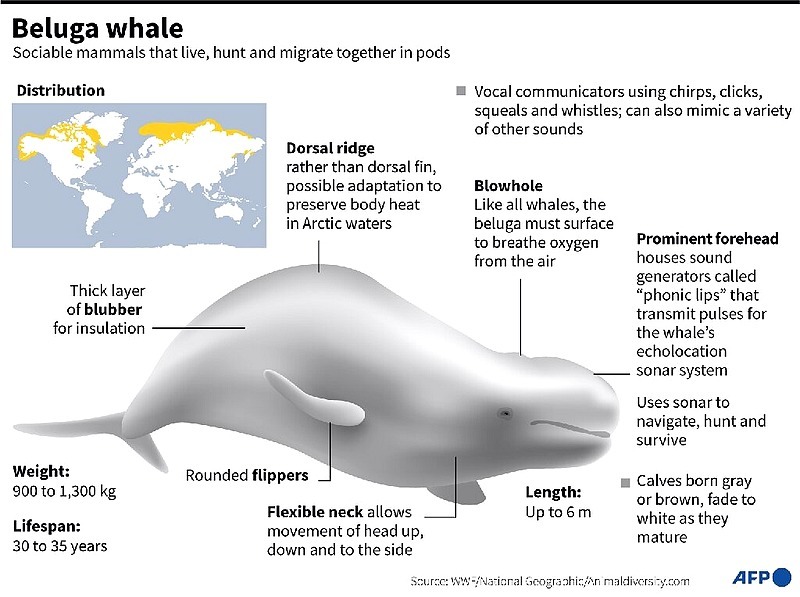
The gray color of the young whales stands out against the bright white adults as they glide through the water in packs, all the while communicating in their own array of sounds.

Hydrophone
Nicknamed “canaries of the sea” due to the 50 or so different vocalizations — whistles, clicks, chirps and squeals — they emit, belugas are “social butterflies” and “sound is the glue of that society,” said Valeria Vergara, who has been studying them for years.
“Belugas are sound-centered species, and sound to them is really like vision to us,” the researcher with the Raincoast Conservation Foundation told AFP.
Listening at the speaker of a hydrophone, the 53-year-old scientist tries to distinguish the multitude of sounds from the depths — a cacophony to the untrained ear.
“They need to rely on sound to communicate and they also rely on sound to echolocate, to find their way… to find food,” said Vergara, who has identified “contact calls” used between members of a pod.
Newborn belugas, which measure around 1.8 meters long and weigh some 80 kilos, remain dependent on their mother for two years.
As an adult, the mammal — which generally matures in the icy waters around Greenland and in the north of Canada, Norway and Russia — can grow to six meters long and live between 40 and 60 years.
The Hudson Bay beluga population is the largest in the world.
But the decrease in ice due to climate change, in an area that is warming three to four times faster than the rest of the planet, is a cause for concern for researchers.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT








































